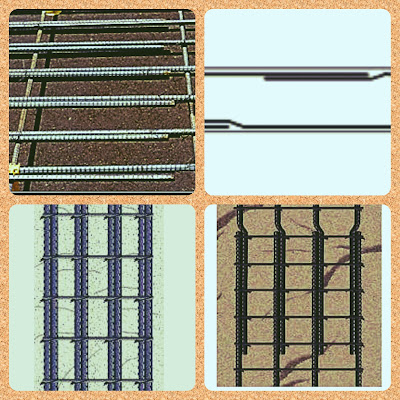
Lapping in Reinforcement
Lapping in Reinforcement: Lapping length of reinforcement is one of the important term in RCC. It is a very confusing term, because most of the professional mixed up lapping length with development length or anchorage length.Steel reinforcement has a limitation in length, usually it is 12.00 meter in length. So in case of RCC structure, placing of a single bar may not meet the required length of the section and it becomes necessary to join two bars, to meet the desire length. To join two bars, one bar should overlap another and it is called lapping of bar and the length overlap each other is caller lap length or overlap length.
Lapping process
Lap length is different for different concrete section. You can find some thumbs formula i,e, 50d or 36d in many website but if you want to follow the ACI code you have the reading material below:
you may like: Clear Cover of Concrete
Lapping process
Calculation of Lapping Length:
Lapping is not permitted for reinforcement greater than No.11
lapping length for longitudinal reinforcements are as follows:
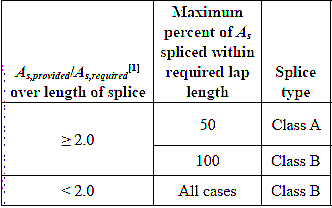
for Class A Splice: Lapping length will be the greater of 1.0Ld and 12 inch.
for Class B Splice: Lapping length will be the greater of 1.3 Ld and 12 inch.
* Here Ld is the development length.
Lapping length for Tension Reinforcement (same as Longitudinal Reinforcement):
for Class A splice: Lapping length will be the greater value of
1.0 Ld and 12 inch.
for Class B splice: Lapping length will be the greater value of 1.3 Ld and 12 inch.
Here Ld is the development length.
Compression Lapping length of No.11 or smaller deformed bar Shall be calculated as :
(a) for fy ≤60,000 psi lapping length is greater of 0.0005 fy*db and 12inch.
(b) for fy > 60,000 psi, lapping length is greater of (0.0009 fy-24)db and 12 inch.
Note: for fc'<3000 psi the length of lapping will be increased by one-third.
compression lapping should not permitted for bar greater than No.11 except permitted at code.
All informations are from ACI Code
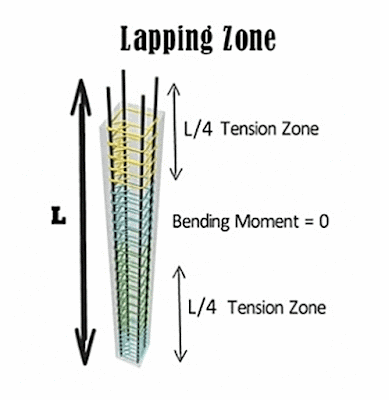
Lapping Zone: For column the lapping zone is middle portion of the column, because the L/4 distance from both support of the column experienced much tension and at the middle point the tension is zero. Since, middle portion experience less tension so it is safe to provide lapping in middle section.
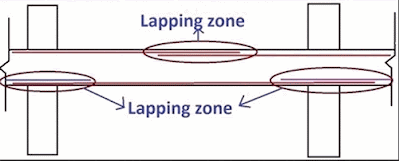
In case of beam, for top reinforcement mid section don't experience any negative moment so it is the safe zone for lapping. For bottom reinforcement, lapping is provided near the end of the beam or L/4 distance from column face.
Frequently asked questions:
What is Lapping in reinforcement?
Ans: When placing of a single bar can not meet the required length of the section and it becomes necessary to join two bars, to meet the desire length. To join two bars, one bar should overlap another and it is called lapping of reinforcement.
Why is lapping used in reinforcement?
Ans: When placing of a single bar can not meet the required length of the section then lapping used to join two bars, to meet the desire length.
Also lapping is required when bar diameter has to be change along the length.