Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
The Standard Penetration Test (SPT) is a dynamic penetration test that is carried out at site. This test is the most frequently used subsurface exploration drilling test performed worldwide. The test will measure the resistance of the soil strata to the penetration undergone. The test shows its extremely usefulness for determining the relative density and the angle of shearing resistance of cohesionless soils. It can also be used to determine the unconfined compressive strength of cohesive soils.
 |
| Fig: Standard Penetration Test (SPT) in Field |
Tools for Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
The equipment’s used to conduct SPT are:
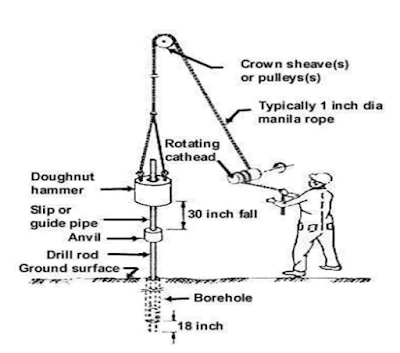
1. Standard Split Spoon Sampler (Outer dia. 50.8mm, inner dia. 35mm and length 650mm)
2. Drop Hammer weighing 63.5kg(140lb)
3. Guiding rod
4. Drilling Rig.
5. Driving head (anvil).
Procedure for Standard Penetration Test:
The test is conducted in a bore hole by means of a standard split spoon sampler .Once the drilling is done to the desired depth, the drilling tool is removed and the sampler is placed inside the bore hole. By means of a drop hammer of 63.5kg(140lb) falling from a height of 750mm(2.5ft), the sampler is driven into the soil. The number of blows of hammer required to drive a depth of 150mm is counted. Further it is driven by 150 mm and the blows are counted. Similarly, the sampler is once again further driven by 150mm and the number of blows recorded. Total 450mm length will be driven and the number of blows required for these penetration will be recorded. The number of blows recorded for the first 150mm not taken into consideration and the number of blows recorded for last two 150mm(150mm+150mm =300mm) intervals are added to give the standard penetration number (N).
If the number of blows for 150mm drive exceeds 50, it is taken as refusal and the test is discontinued.
Corrections in Standard Penetration Test:
Before the SPT values are used in empirical correlations and in design charts, the field ‘N’ value have to be corrected as per IS 2131 – 1981. The corrections are:
1. Dilatancy Correction
2. Overburden Pressure Correction
Advantages of Standard Penetration Test
The advantages of standard penetration test are:
1. The test is simple and economical
2. Test can be applied for variety of soil conditions
3. The test provides representative samples for visual inspection, classification tests and for moisture content.
4. Actual soil behaviour is obtained through SPT values
5. The method helps to penetrate dense layers and fills
Disadvantages of Standard Penetration Test
The limitations of standard penetration tests are:
1. Test is costly and time consuming.
2. The samples retrieved for testing is disturbed.
3. The results will vary due to any mechanical or operator variability or drilling disturbances.
4. The test results from SPT cannot be reproduced
5. The application of SPT in gravels, cobbles and cohesive soils are limited








